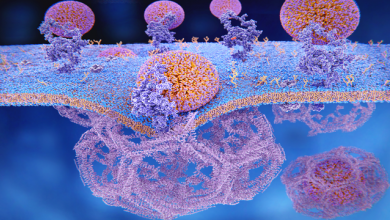
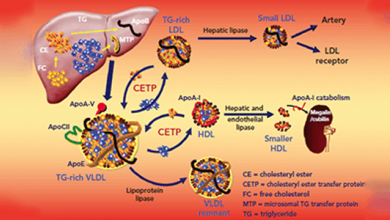
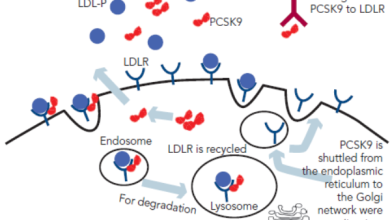
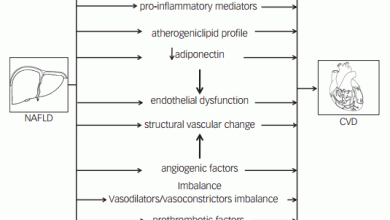
Substantial progress in the treatment of atherosclerotic complications – in particular in secondary prevention – has led to a significant reduction of recurrent cardiovascular events. This has been through the use of pharmacological strategies including lipid-lowering drugs such as statins, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting ensyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers, along with the introduction of early percutaneous coronary intervention in acute coronary syndrome with consecutive application of dual antiplatelet therapy.
Close Menu
View all - Electrophysiology & Arrhythmia
Atrial Arrhythmias
Atrial Fibrillation
Catheter Ablation of Cardiac Arrhythmias
Persistant AF using Cryoballoon
Real World Contact Force Ablation
Pacing, Defibrillators and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy
Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation
Ventricular Arrhythmias
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Sudden Cardiac Death
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
About
Media
Watch time: 4m 57s
Articles
Statins and Insulin Resistance
Citation:
European Cardiology Review 2020;15:e44.
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 4
4
- Downloads:
 0
0
Role of PGC-1-alpha-associated Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Statin-induced Myotoxicity
Citation:
European Cardiology Review 2020;15:e35.
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 4
4
- Downloads:
 0
0
- Citations: 2
Anticoagulation in Patients with Ischaemic Heart Disease and Peripheral Arterial Disease: Clinical Implications of COMPASS study
Citation:
European Cardiology Review 2018;13(2):115–8.
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 679
679
- Downloads:
 0
0
- Citations: 6
Using Pharmacogenetic Testing or Platelet Reactivity Testing to Tailor Antiplatelet Therapy: Are Asians Different from Caucasians?
Citation:
European Cardiology Review 2018;13(2):112–4.
- Abstract
- Full text
- Login or register to view PDF.
- Permissions
- References
Permissions×
For commercial reprint enquiries please contact Springer Healthcare: ReprintsWarehouse@springernature.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
For permissions and non-commercial reprint enquiries, please visit Copyright.com to start a request.
For author reprints, please email rob.barclay@radcliffe-group.com.
- Views:
 259
259
- Downloads:
 0
0
- Citations: 8